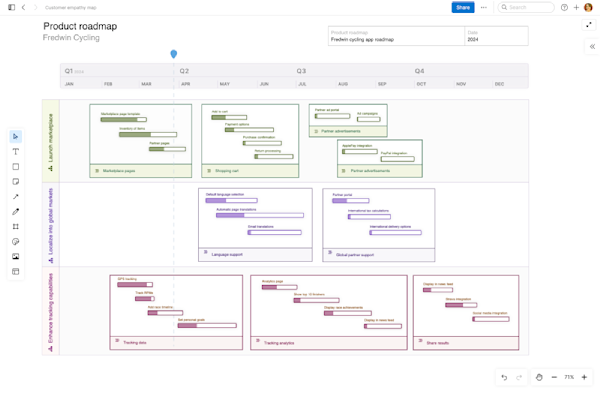
What is product development?
An essential guide for product managers
Last updated: September 2025
Product development is the end-to-end process of creating and improving products — from strategy and discovery through delivery, launch, and ongoing analysis. It defines why you are building, what you will deliver, and how teams will collaborate to make it happen. This guide explains the 10 stages of the product development process, the roles involved, and frameworks you can use to structure the work (including The Aha! Framework.) |
Product development is the ongoing process of creating and improving products to deliver value to customers. It begins with strategy and discovery, moves through ideation to roadmapping and planning, and results in new or enhanced functionality that product teams deliver and launch into the market. The product development process continues as teams gather feedback to improve the offering over time.
Whether you are introducing a brand-new offering or improving an existing product, the product development process is about much more than "how" a product is built. It also involves the "why," "what," and "when" — encompassing cross-functional work from product management and engineering all the way to product marketing. Your goal is to work together to build, launch, and refine a product that customers love.
Streamline product development with Aha! software — sign up for a trial.
In this guide, you will learn the fundamentals of product development: everything that goes into shaping a product that drives meaningful impact and delivers lasting value.
What are the stages of product development?
No two organizations build products in exactly the same way. But there are standard stages that nearly all teams cycle through, from setting strategy to analyzing success. You typically complete one stage before moving to the next, but you can refine decisions and solutions throughout the entire product development process.
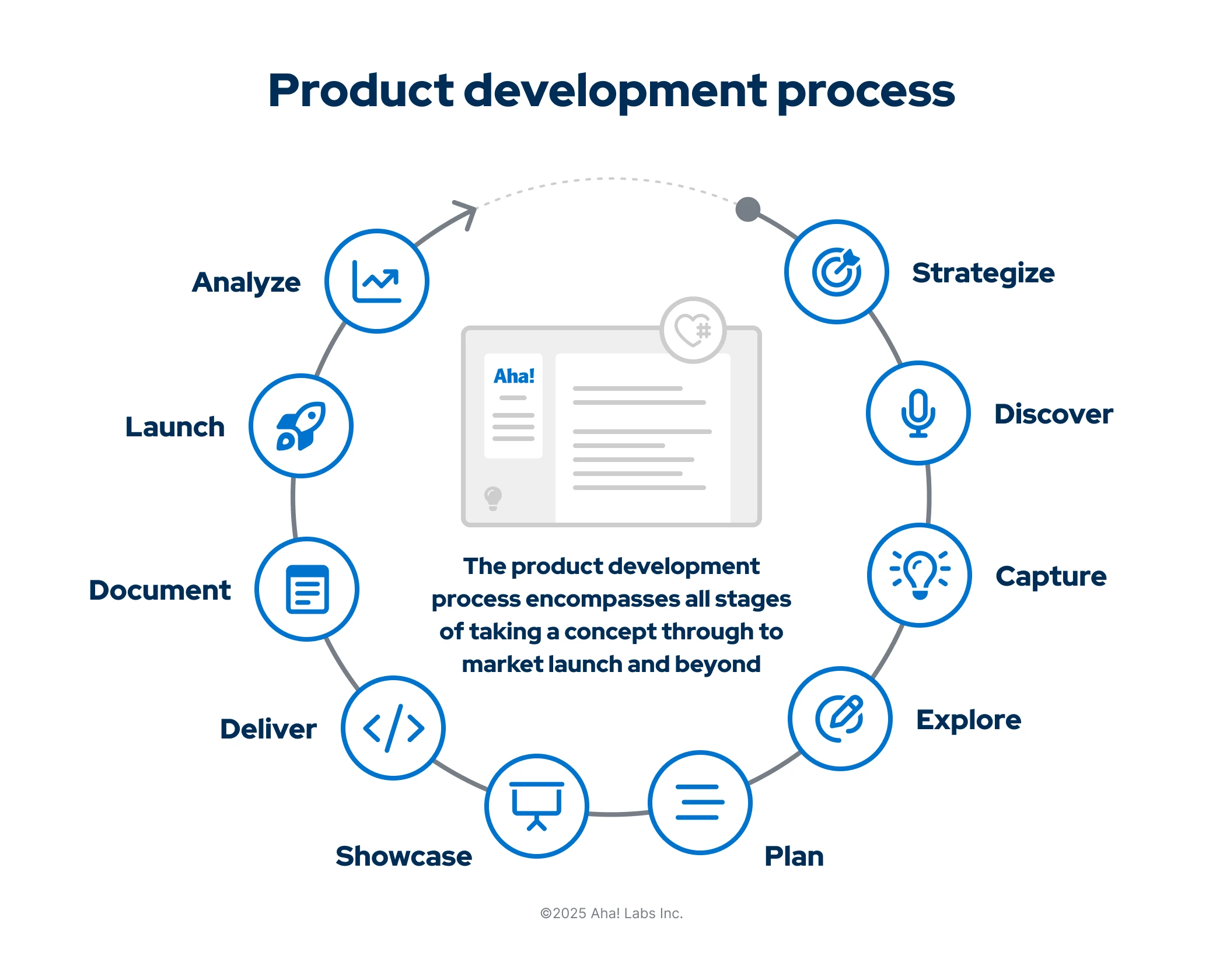
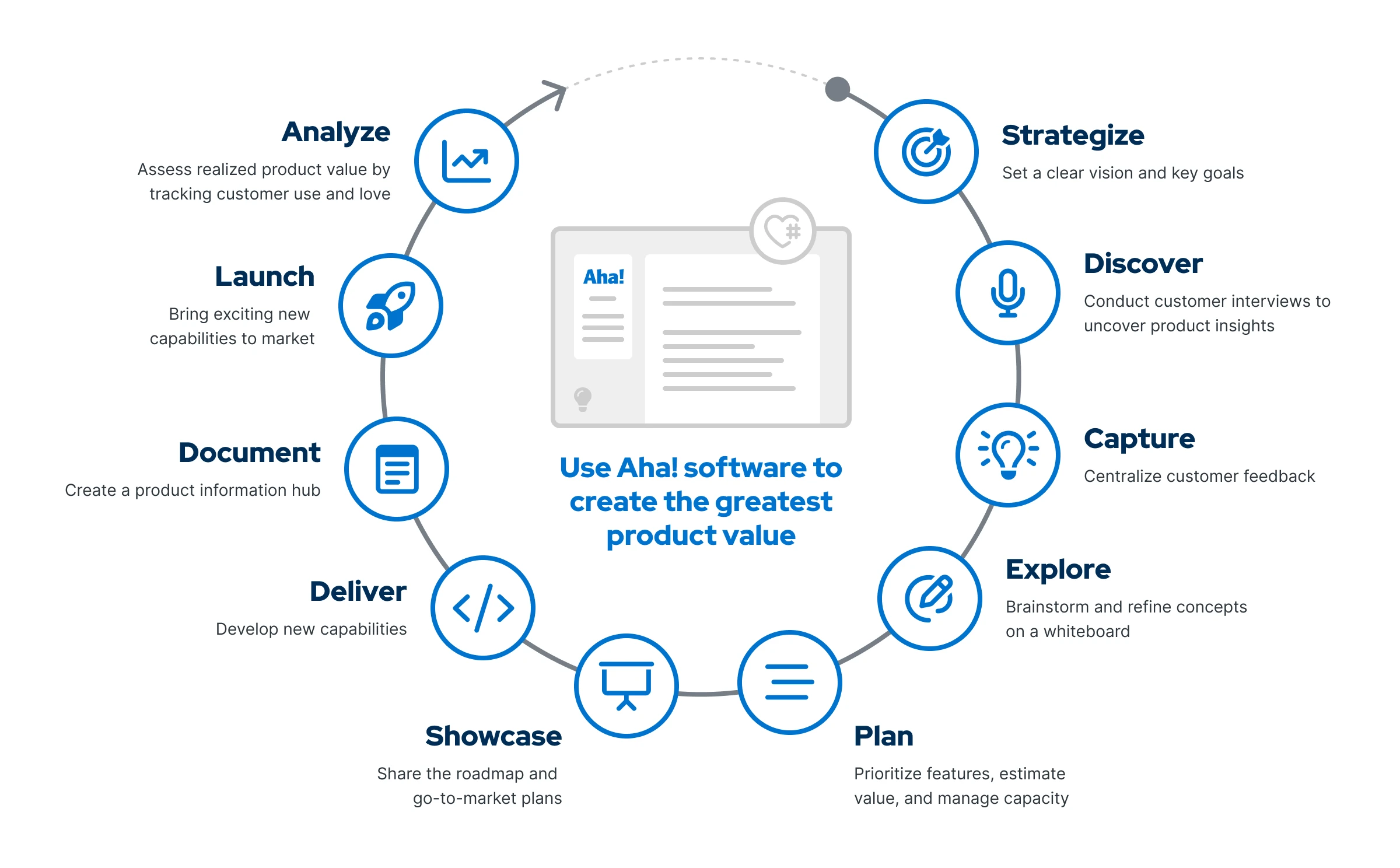
These are the 10 stages of the product development process:
Strategize: Define goals and initiatives.
Discover: Conduct customer interviews to uncover key product insights.
Capture: Streamline customer feedback and collect promising ideas.
Explore: Brainstorm and refine ideas on a whiteboard.
Plan: Prioritize ideas based on strategic goals, estimated product value, and team capacity.
Showcase: Share roadmaps and go-to-market plans with stakeholders.
Deliver: Deliver functionality and supporting work across teams.
Document: Centralize product knowledge for internal teams and customers.
Launch: Bring those exciting new capabilities to market.
Analyze: Assess realized product value by tracking customer usage and love.
Related:
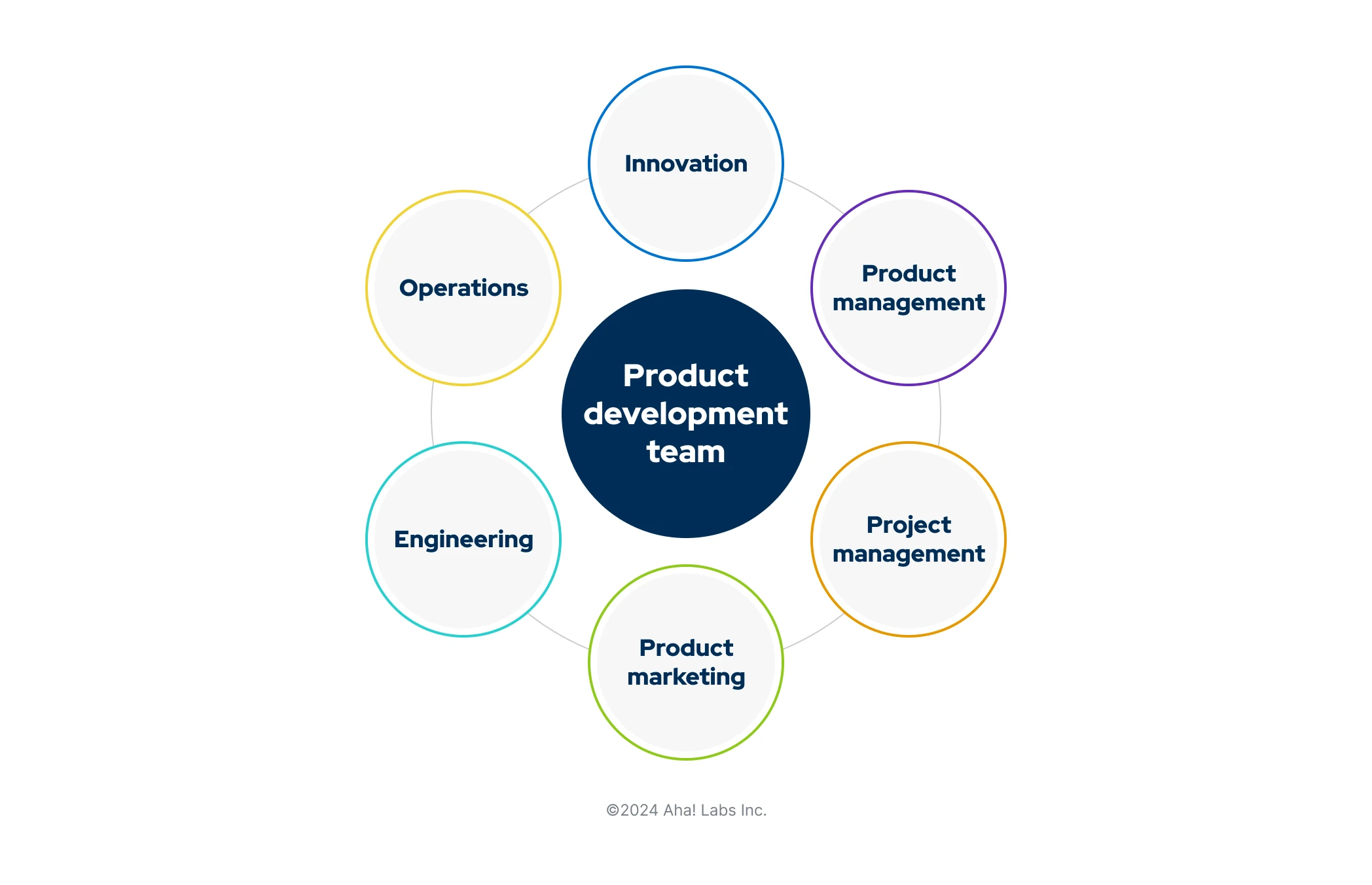
Which teams participate in product development?
As a product manager, you guide the product's success. You set product strategy, build the roadmap, and define product features. And you sit at the center of the cross-functional product team: folks from across the organization who contribute to delivering the product. This typically includes representatives from project management, product marketing, engineering, operations, and innovation.
Every organization defines its product development team differently, depending on its product and industry. But this group often made up of people actively involved in the stages of product development. This team also collaborates with other stakeholders who participate in the product's success as well — think customer success, sales, finance, and legal. Everyone in a product-led organization plays an important role in understanding customers and delivering a Complete Product Experience.