How product managers gather and use customer feedback
Learn how to capture what matters — from incoming ideas to intentional conversations
Last updated: June 2025
Learn how to collect, analyze, and act on customer feedback (including insights from ideas, support tickets, interviews, and usability tests). Discover how top product teams use Aha! software to connect customers' needs to strategic product planning. |
Customer feedback is the backbone of good product decisions. It fuels your thinking early on and keeps you grounded as the product evolves. You might learn how people feel about a new feature, challenge assumptions about user behavior, or uncover needs you had not anticipated.
But feedback is not just a path to better outcomes. It is also a way to build trust. Listening shows people you value their perspective. That trust builds stronger relationships — bringing customers back with more insight to share.
Aha! software helps product teams manage the full spectrum of customer feedback.
That said, the real challenge is not collecting feedback, is it? Feedback is everywhere. Product managers are inundated with ideas, requests, complaints, and questions scattered across portals, emails, call notes, and online chats. The hard part is knowing what to pay attention to. What is a passing comment vs. a real problem? Which voices represent broader trends?
This is where structure matters. Without it, valuable insights get buried or overlooked. You need a way to capture what is coming in, make sense of it, and tie everything back to what you are building.
This guide walks through how to do that well, and how tools like Aha! Discovery and Aha! Ideas support every part of the customer feedback process. Keep on reading, or use these links to jump ahead to any section:
Customer feedback in product development
Customer feedback includes anything that reveals what people think, want, or need from your product. It might come through a support ticket, an idea submission, or a quick note during a call. This feedback gives you a window into how users feel and why they behave the way they do.
And inputs show up in all kinds of ways. An ideas portal reveals common requests and patterns over time. 1:1 conversations uncover nuances you cannot get at scale. Product analytics show how people actually interact with your product — pointing to areas that might deserve further exploration.
At Aha! we view feedback and discovery as a connected system. Aha! Ideas helps you capture and analyze feedback, offering you a broad view of what people are asking for. Aha! Discovery helps you dig deeper, plan research studies, and link insights directly to your roadmap. Together, the tools help you move from input to insight to strategic action.
Related:
What should you consider before collecting customer feedback?
Strategic product managers do not gather feedback just to hear what people think — they do it to learn something specific. Clarity of purpose is everything. When you know what you want to understand, it is easier to identify the right audience, choose the best research methods, and recognize meaningful insights when you hear them.
To stay organized, set up a simple system to track:
Who shared input: Use tags like role, industry, or usage level.
Why it matters: Tie each interaction to a clear learning goal.
What was shared: Link insights to related ideas or upcoming work.
Build your own customer database to manage who to engage with based on their persona or interests.
Choose the feedback method based on what you want to learn. If you need depth, try interviews. A survey might be a better fit if you want quick input from a wider group. We break down these options in the next section.
What are some methods for collecting customer feedback?
You have more ways than ever to gather customer feedback, but that does not make it easier to know where to start. Below are the most common approaches organized into three categories: always-on listening, structured discovery work, and quantitative signals.
Always-on listening
These channels stay open around the clock. Feedback flows in, but it takes effort to spot the themes worth acting on.
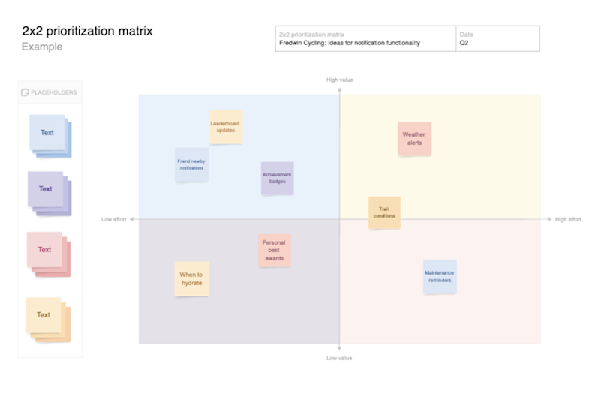
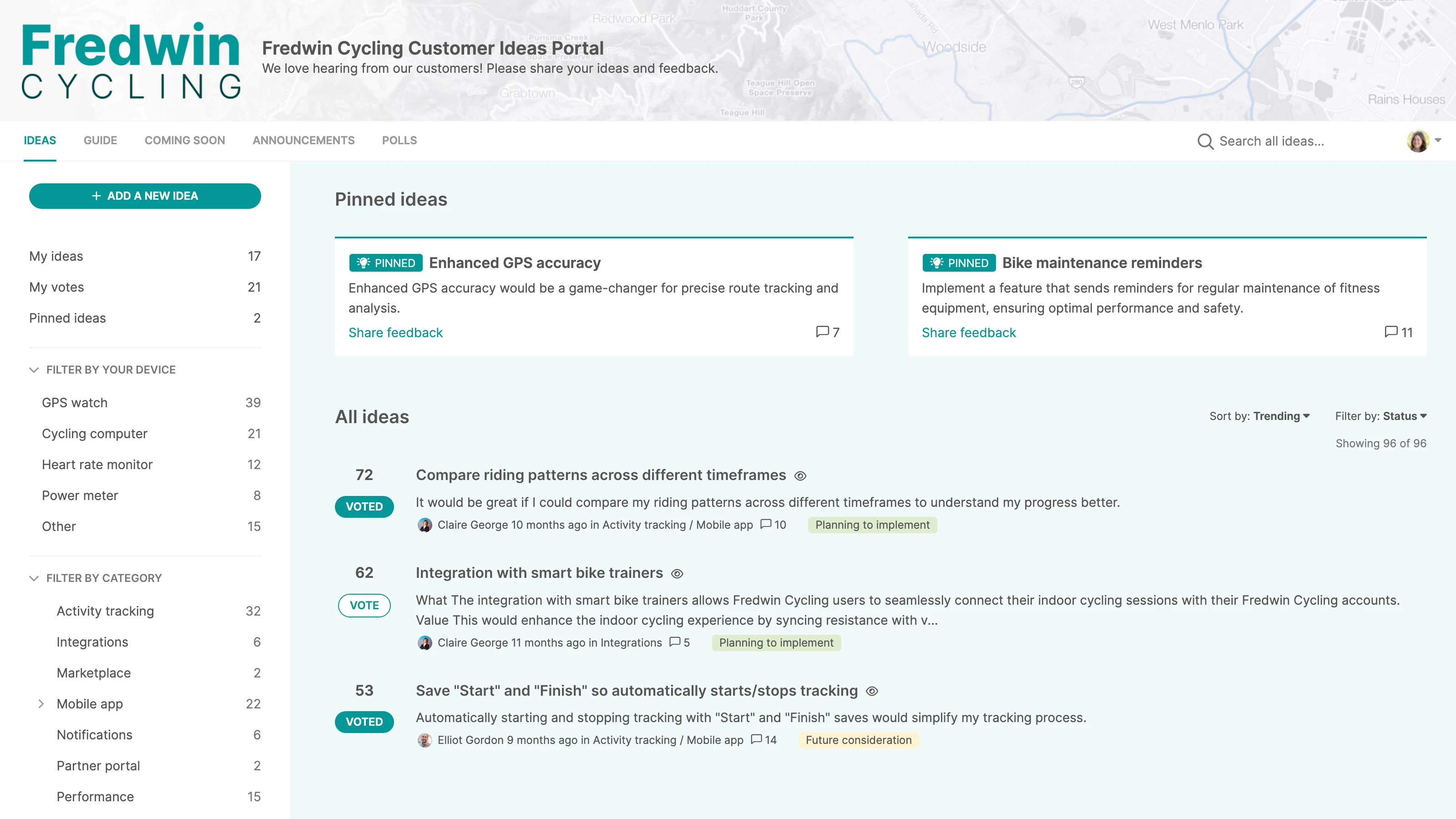
Ideas portal | Give customers a place to submit suggestions, requests, and pain points. With Aha! Ideas, you can crowdsource feedback, identify trends, and evaluate what matters most using voting and proxy voting. Use it when: You want a scalable, always-on way to collect and prioritize feedback over time |
Support tickets and sales notes | Customer-facing teams hear about user needs every day. Capturing these insights — and tying them to product requests — brings context to your roadmap planning. Use it when: You want to spot recurring pain points or understand the "why" behind common friction |
Community forums and social media | People do not always reach out directly, but they often share what they think. Online discussions and social media posts can surface issues, ideas, or unexpected use cases. Actively monitoring these channels helps you understand what users are talking about and where friction might be hiding. Use it when: You want to track unfiltered reactions and uncover emerging issues or themes |