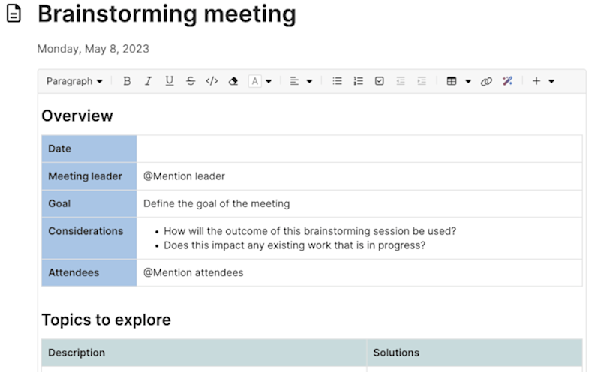
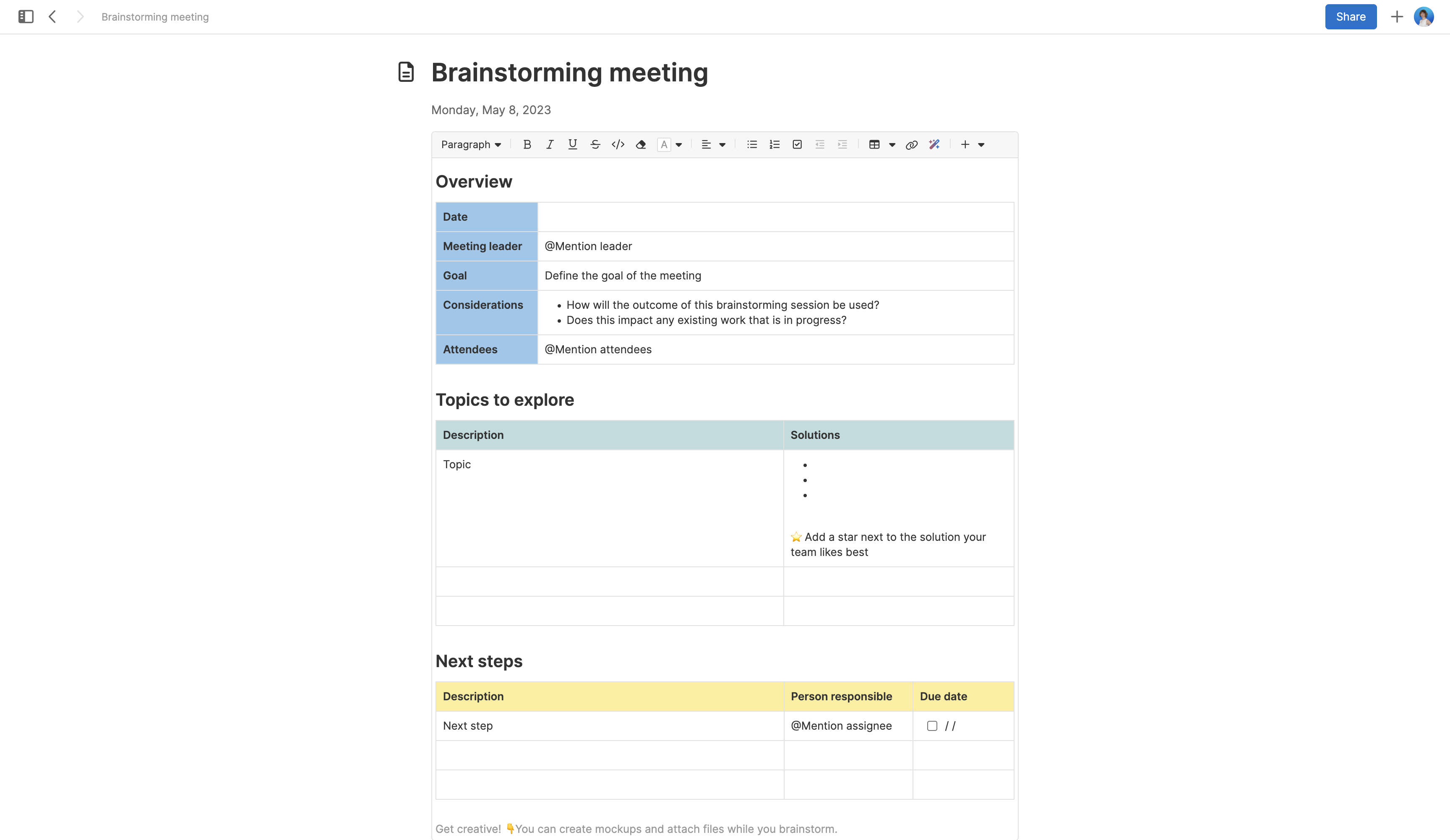
In this guide, we will share some tips for brainstorming sessions that yield the best outcome for your product, your customers, and your team. Jump ahead to any section:
Is brainstorming important for product development?
Product development is the entire process of bringing new ideas to life. These teams are tasked with finding clever solutions to challenges by problem-solving for customers and for the company. Generating new ideas is essential for success.
This makes brainstorming an important activity in early-stage product development. The key is to explore and refine concepts in a thoughtful way (rather than adopting a freewheeling, say-yes-to-everything approach). Product development teams typically benefit from a more structured method. So your brainstorming sessions should be oriented around offering suggestions that present actual opportunities to innovate based on the overall product direction.
Product managers typically lead these sessions and are responsible for offering strategic context, asking follow-up questions, and documenting everything that is shared. Another way product managers can facilitate is by keeping the conversation focused on generating ideas — if the conversation derails or the team starts to spend too much time discussing one concept, direct everyone back to the agenda.
Remember: A list of ideas is only useful if you have a way to objectively evaluate and implement the best ones. Following an agreed-upon prioritization process is the secret ingredient for turning a brainstorm into a breakthrough.
Related:
Examples of effective brainstorming techniques
Ideas are the result of an open dialogue that reveals a new way to solve a problem. Creating the right circumstances for these conversations to take place is a critical part of any brainstorm. Here are a few examples of popular brainstorming techniques that can be effective for product teams:
Brainwriting: Write down ideas silently, then pass them to the person on the left or right. Each person adds additional thoughts to the concept as bullet points. At the conclusion, the original ideator shares the built-out concept with the group.
Figurestorming: View the problem through the lens of a relevant public figure (for example: "How would Steve Jobs fix this?"). You can also ask from the perspective of a user or buyer persona the team has already defined.
Mind mapping: Starting with one concept on a whiteboard or piece of paper, have the team add related subconcepts as spokes that spider out from the central idea. The result is a visual mind map.
Rapid ideation: Churn out as many ideas as possible within a specific time frame. The goal is to capture high-level concepts and not censor your own creative process.
Round robin/musical chairs: Swap people in and out of ideation groups at set intervals over a period of time. Each newly formed group contributes to building out the concept.
Related:
Top
How to run a product brainstorming session
There might not be any "bad" ideas in a brainstorm, but there are certainly bad brainstorming meetings. Failed brainstorms happen for a variety of reasons, ranging from poorly formed focus questions to a lack of diversity in attendees to ideas being shot down by the organizer. Most of us tend to avoid conflict as well. This means you can end up with a list of many similar ideas because people felt comfortable conforming to groupthink rather than voicing different concepts.
But a productive brainstorming session is different. It can be exhilarating. Attendees feel satisfied after contributing their creative input, and the product development team has a long list of ideas to investigate further. So how do you structure your time to be most effective?
The exact parameters of your product brainstorming meeting will depend on a variety of factors — from the scope of the problem you are hoping to solve to the maturity of your product. However, there are a few consistent factors to be aware of when organizing your product brainstorm meeting.
Who to invite
First, you want to bring in the right people. Product brainstorming meetings can include internal or external stakeholders. Examples of internal stakeholders include cross-functional teammates from departments such as engineering, marketing, sales, and support. These folks typically have different backgrounds, knowledge of your product, and level of exposure to customers. So a diverse mix of internal sources can result in a high-yield brainstorm.
Your external stakeholders could be current customers, partners, or a focus group of people who represent your product's users. With external stakeholders, you always want to consider how familiar the attendees are with your market and offering — you might need to provide additional context depending on who you choose to include.
As for your group's size, traditional brainstorming sessions cap group members at six to 12 people. Any more, and you might miss out on quieter voices and lose track of the group. Any less, and you might miss out on the potential for "piggybacking."
Where to host it
You probably know the cliche image of a conference room with sticky notes plastered all over a whiteboard. Although once synonymous with brainstorming, this style of in-person meeting is no longer the best way to structure your brainstorming session. This old-fashioned approach puts undue pressure on the product manager to record everything that is said and risks your ideas getting erased or lost.
This is why many product teams choose purpose-built whiteboard software that offers more streamlined virtual brainstorming. With built-in templates, diagramming capabilities, and fun collaboration tools (such as emoji reactions), whiteboard software helps make any brainstorming session more effective and enjoyable
How to prepare
Product managers are responsible for setting the brainstorm's context and creating an agenda. To prepare, you should set the objective for the session, gather related materials, and formulate prompts to keep the conversation going.
Your objective should be simple to understand and can be a touchstone for reorienting the conversation if people get sidetracked. Examples of objectives for product brainstorming include:
Related materials should be kept to a minimum (but still available for the group's reference). The materials you provide will depend on the brainstorm's goal, but some common sources of inspiration include:
Product positioning and customer personas
Research and customer feedback
Competitive analysis and industry trends
Past performance data (e.g., usage metrics or feature adoption)
Mockups or wireframes
Encouraging participants to review relevant information ahead of time can help spark ideas. You can also document open-ended prompts in advance to guide the conversation. Consider sharing questions like:
How do people solve this problem using our product right now?
What would happen if we did not solve this problem for customers?
What trends or competitor moves should we consider?
More tips for brainstorming sessions
Brainstorming is a creative process. Keep these tips top of mind when getting ready to brainstorm product ideas:
Reference product strategy.
Invite a diverse group and give people time to prepare.
Create a supportive environment.
Articulate the problem clearly and provide needed context.
Set a time limit.
Introduce visuals — such as shapes, colors, and media.
Be curious; ask questions.
Avoid cross talk.
Group similar concepts into themes.
Get aligned on the best ideas.
Follow up with attendees.
You do not want to create too many rules or stifle the group's imagination. Following the above tips can benefit all teams — no matter what type of product you are building.
And remember: Great ideas do not just happen during meetings. Keep the flow of inspiration going by making it easy for folks across the company to share their thoughts. Ensure other teams in the organization know about your ideas portal, and look for organic ways to gather input. This might mean chatting with sales about customer objections, checking in with support on top requests, or seeing what trends marketing is tracking. Fresh perspectives often lead to better ideas.
Top
Brainstorming templates to get started
Folks who use the Aha! software suite can work from pre-built whiteboard templates to facilitate a brainstorming meeting and host a brainstorming session. They can also try out different brainstorming techniques, including concept mapping, mind mapping, and problem framing.
Try the brainstorming meeting template.